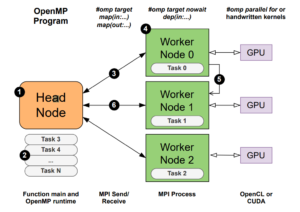
Despite the various research initiatives and proposed programming models, efficient solutions for parallel programming in HPC clusters still rely on a complex combination of different programming models (e.g., OpenMP and MPI), languages (e.g., C++ and CUDA), and specialized runtimes (e.g., Charm++ and Legion). On the other hand, task parallelism has shown to be an efficient and seamless programming model for clusters. This paper introduces OpenMP Cluster (OMPC), a task-parallel model that extends OpenMP for cluster programming. OMPC leverages OpenMP’s offloading standard to distribute annotated regions of code across the nodes of a distributed system. To achieve that it hides MPI-based data distribution and load-balancing mechanisms behind OpenMP task dependencies. Given its compliance with OpenMP, OMPC allows applications to use the same programming model to exploit intra- and internode parallelism, thus simplifying the development process and maintenance. We evaluated OMPC using Task Bench, a synthetic
benchmark focused on task parallelism, comparing its performance against other distributed runtimes. Experimental results show that OMPC can deliver up to 1.53x and 2.43x better performance than Charm++ on CCR and scalability experiments, respectively. Experiments also show that OMPC performance weakly scales for both Task Bench and a real-world seismic imaging application.